Species identification
The species identification tool extracts ribosomal MLST alleles from genomes and determines the species based on the count of alleles that are uniquely found within a single species (or higher taxonomic rank if alleles unique to a species are not found). This is done by making a query to the rMLST genome database.
The tool can be accessed by selecting the ‘Analysis’ section on the main contents page.
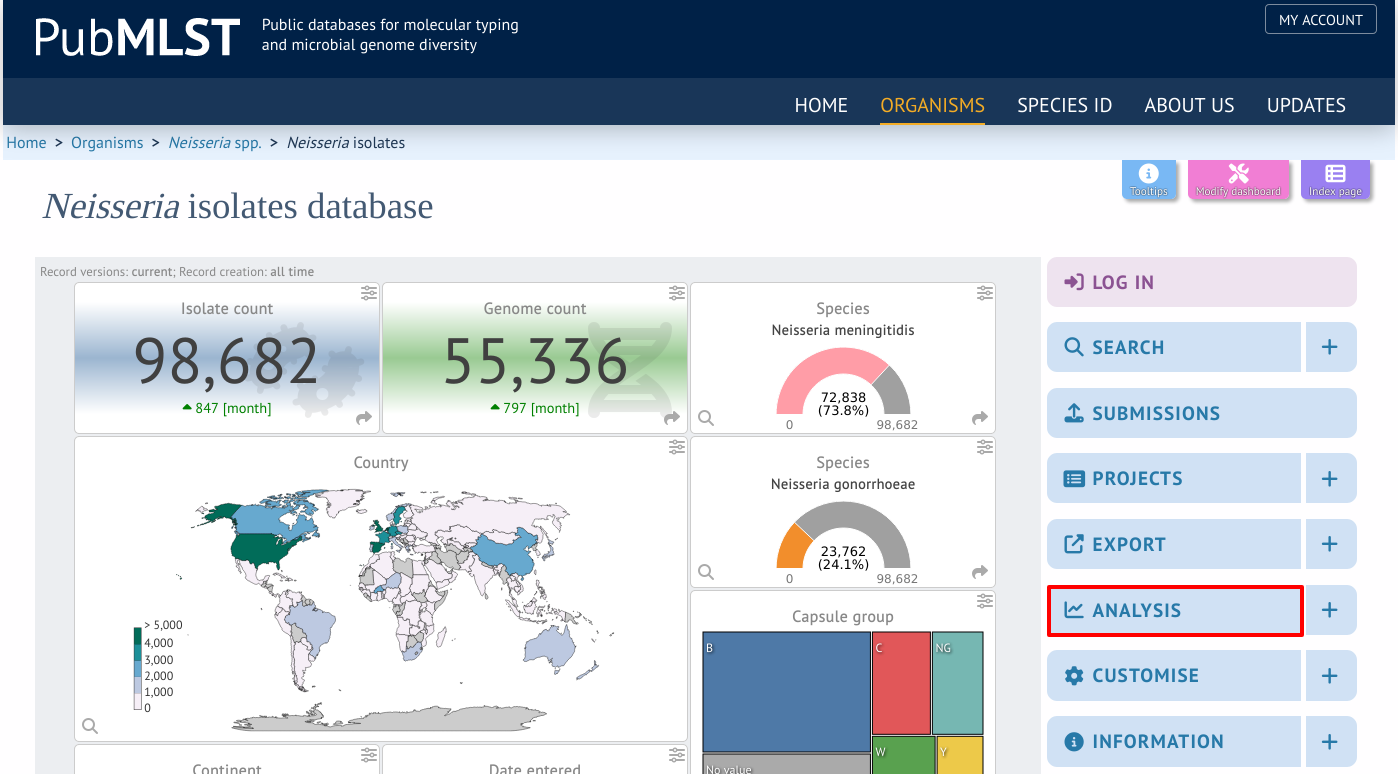
Jump to the ‘Analysis’ category, follow the link to rMLST species identity, then click ‘Launch rMLST species identity’.
The tool can be accessed from the front page of an isolate database.

Alternatively, it can be accessed following a query by clicking the ‘rMLST species id’ button at the bottom of the results table. Isolates returned from the query will be automatically selected within the species id interface (note that only isolates with a genome assembly will be able to be checked).
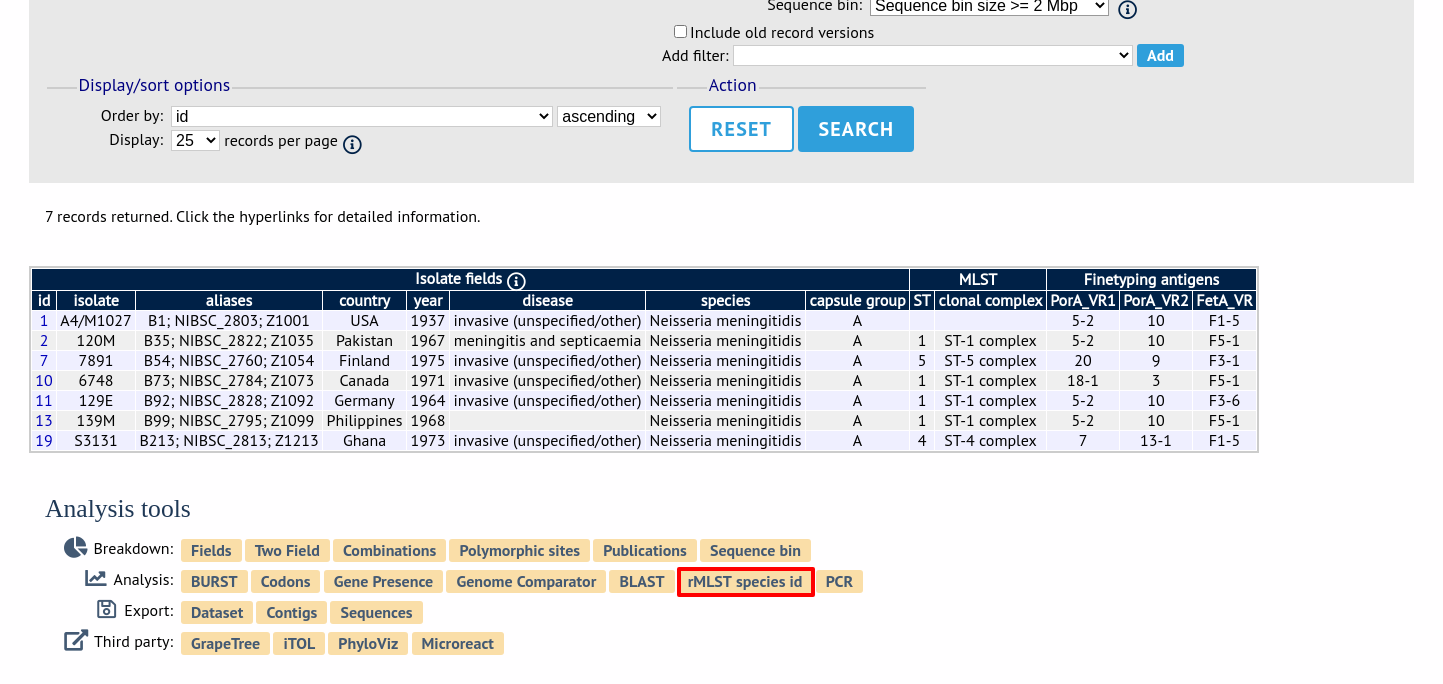
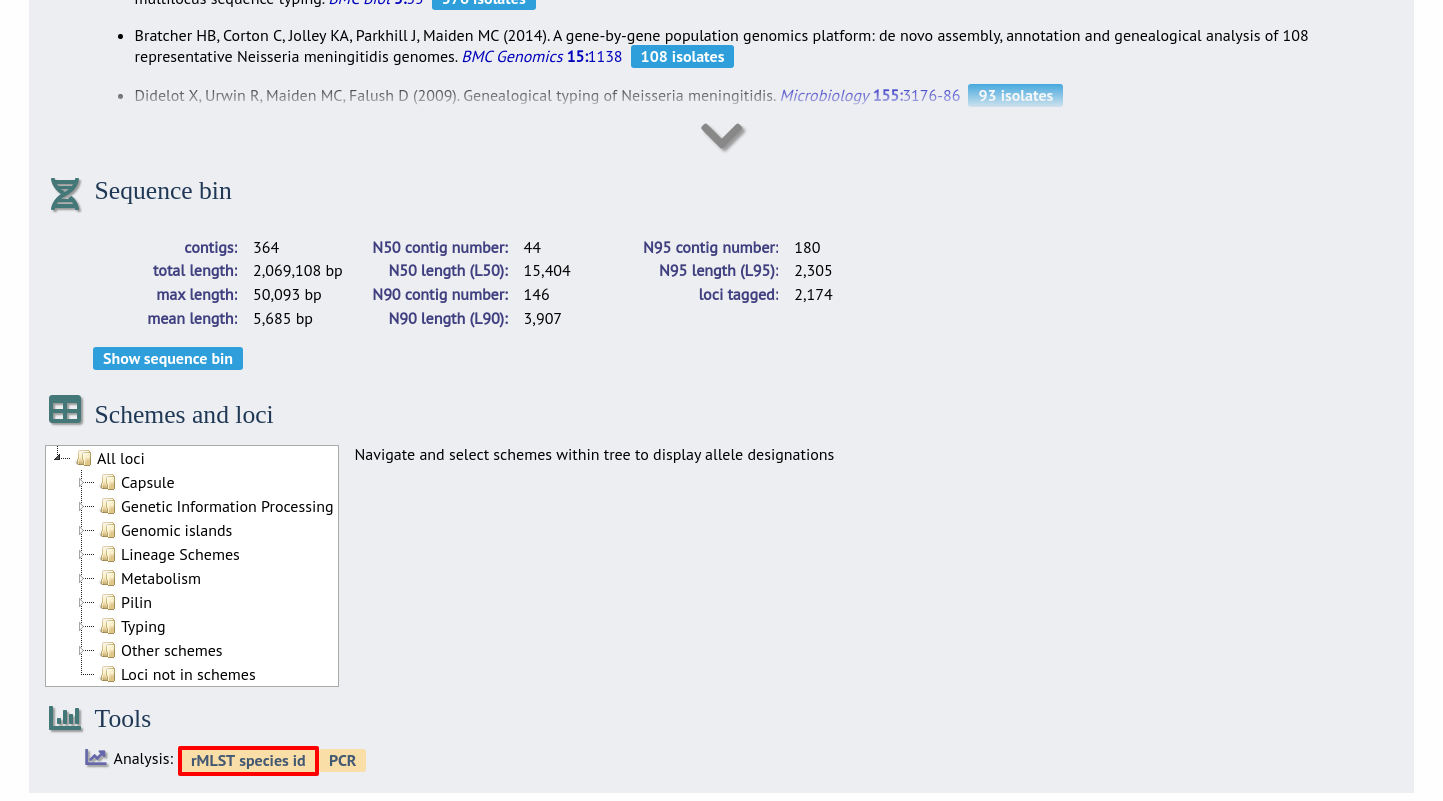
Finally, the analysis is also possible directly from an isolate record, if the isolate has a genome assembly associated with it.
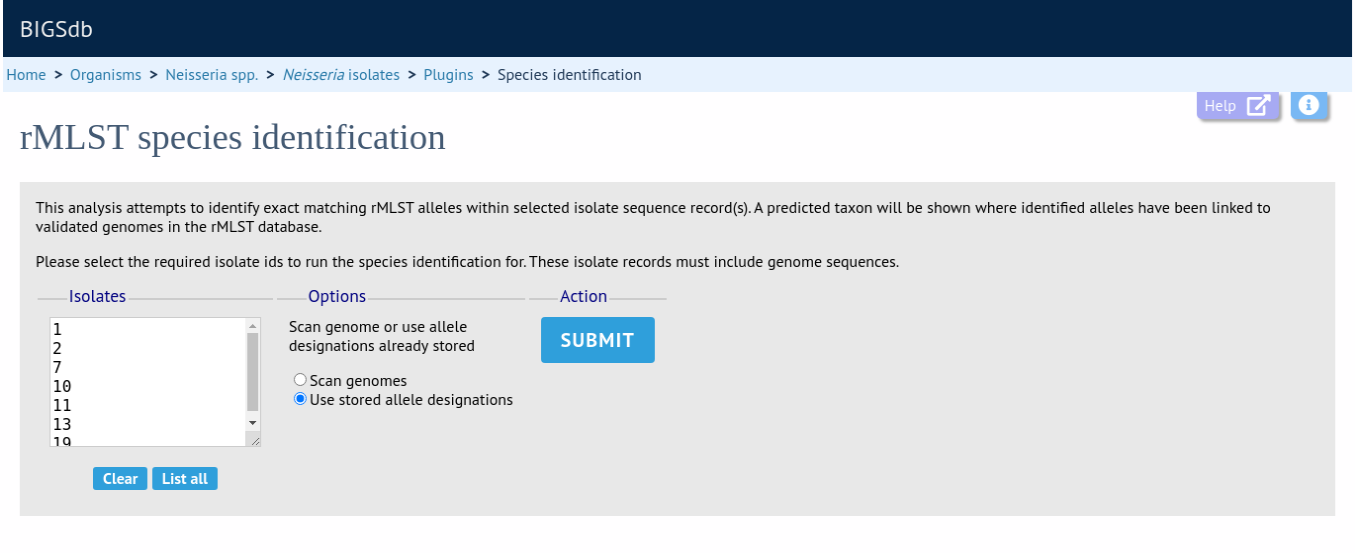
The tool interface consists of a list of isolate ids to check. This will be pre-populated if accessed following a query or directly from an isolate record. If the rMLST scheme is defined on the system, you will have a choice as to whether to BLAST the genome sequences to identify the rMLST alleles, or just use the designations that are tagged in the database. The latter is much quicker but relies on the record having been scanned and annotated with the rMLST loci.
Click ‘Submit’.
The job will be sent to the job queue.
Results will be displayed in a table as they are generated. The table will display the highest taxonomic rank that can be reliably identified, e.g. species, the taxon and its full taxonomy. An indication of the confidence for the result will also be displayed - this is based on the proportion of alleles found that are unique to a taxon.
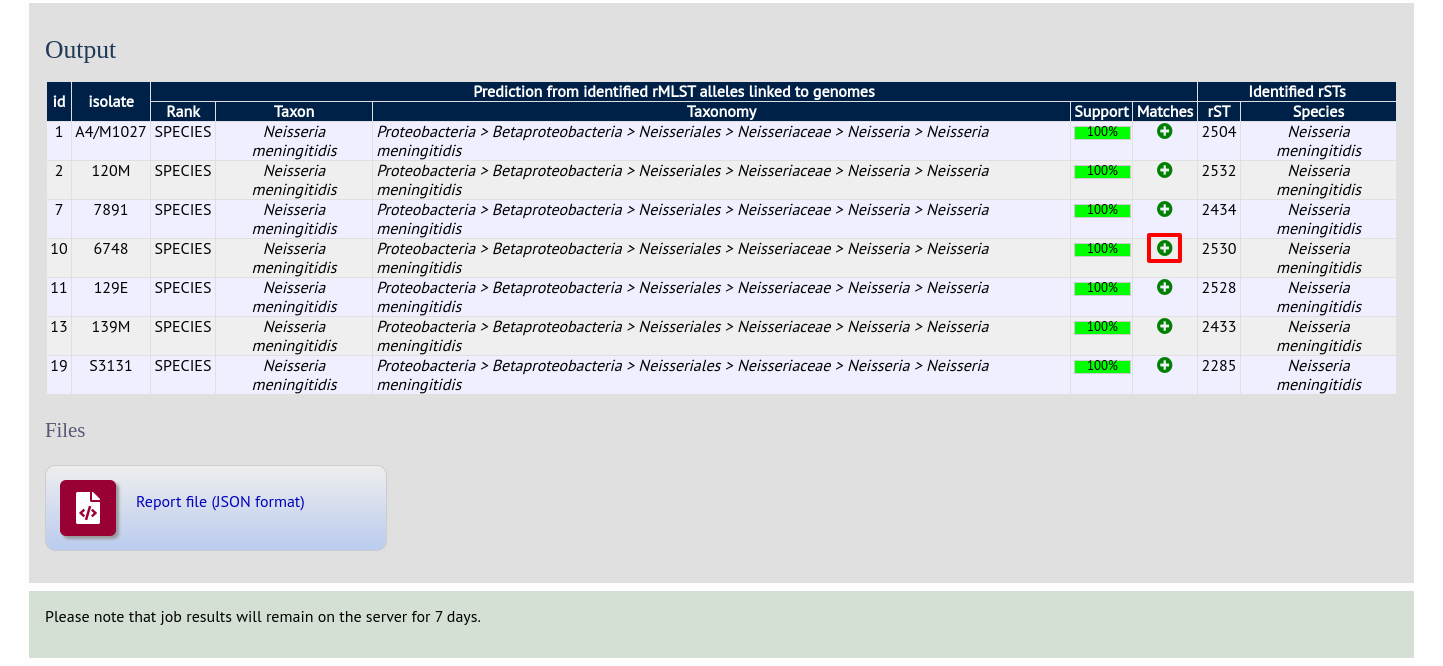
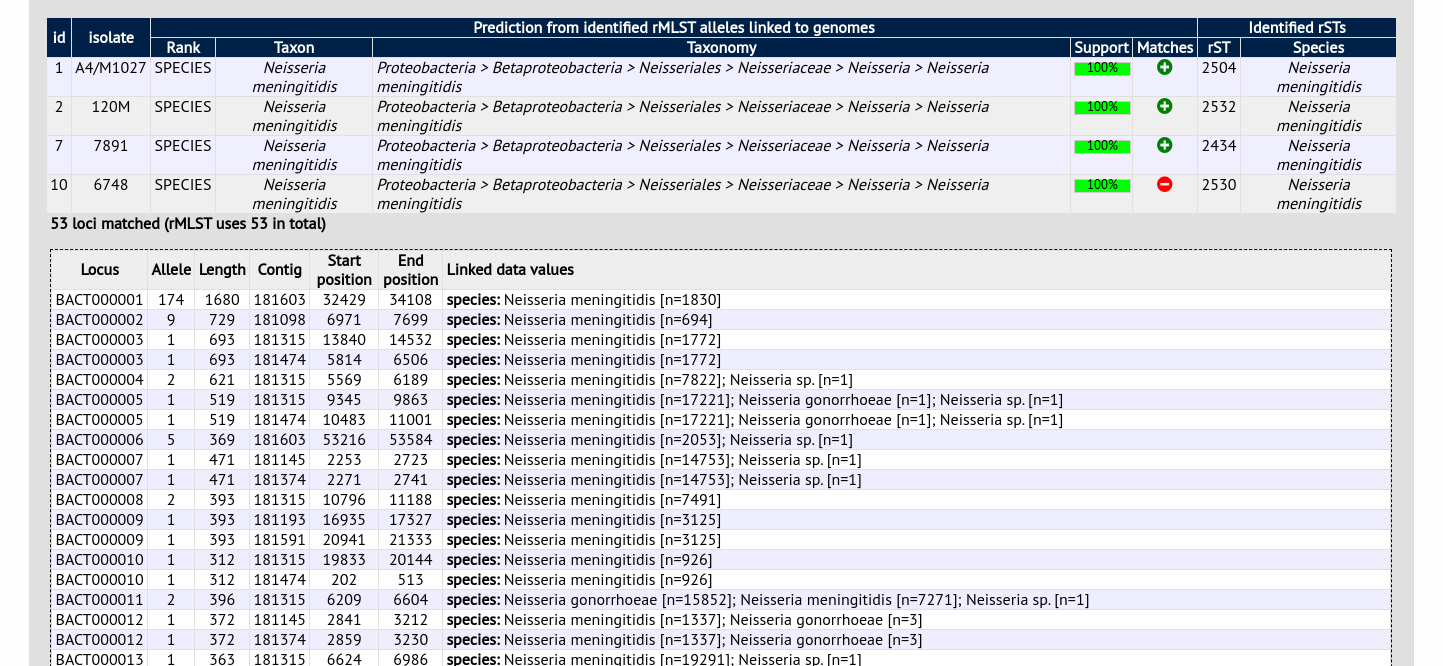
Clicking the ‘+’ icon on any row will display further details about the matches.
Note
Ribosomal MLST was first described in Jolley et al. 2012. Ribosomal multilocus sequence typing: universal characterization of bacteria from domain to strain. Microbiology 158:1005-15