Genome comparator
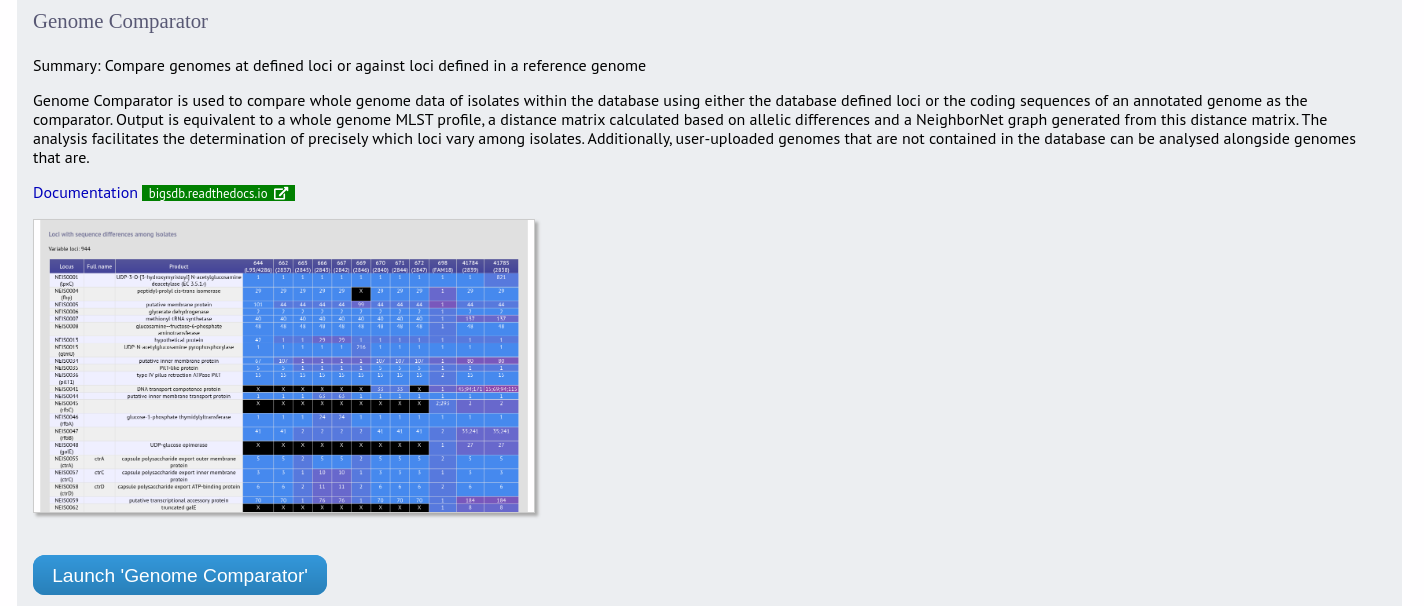
Genome Comparator is an optional plugin that can be enabled for specific databases. It is used to compare whole genome data of isolates within the database using either the database defined loci or the coding sequences of an annotated genome as the comparator.
Output is equivalent to a whole genome MLST profile, a distance matrix calculated based on allelic differences and a NeighborNet graph generated from this distance matrix.
Genome Comparator can be accessed by selecting the ‘Analysis’ section on the main contents page.
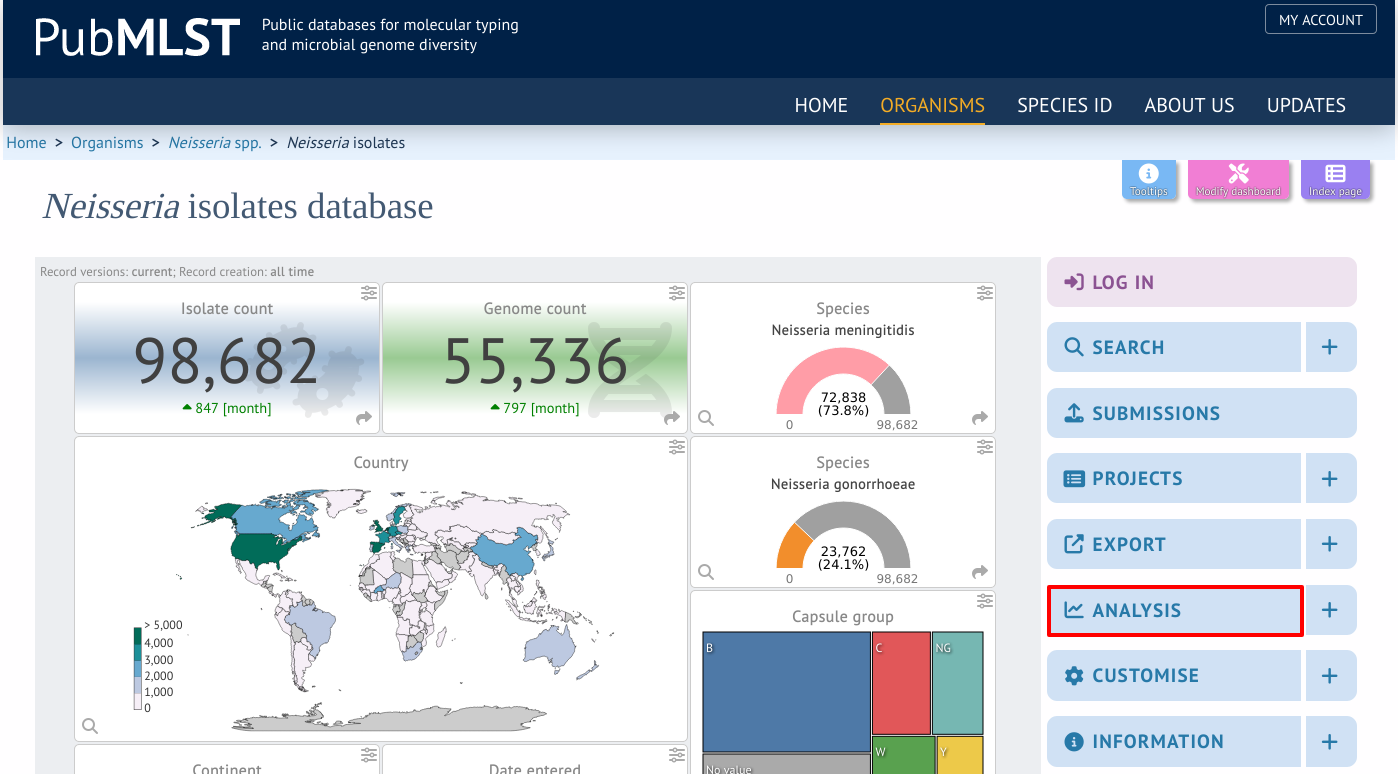
Jump to the ‘Analysis’ category, follow the link to ‘Genome Comparator’, then click ‘Launch Genome Comparator’.
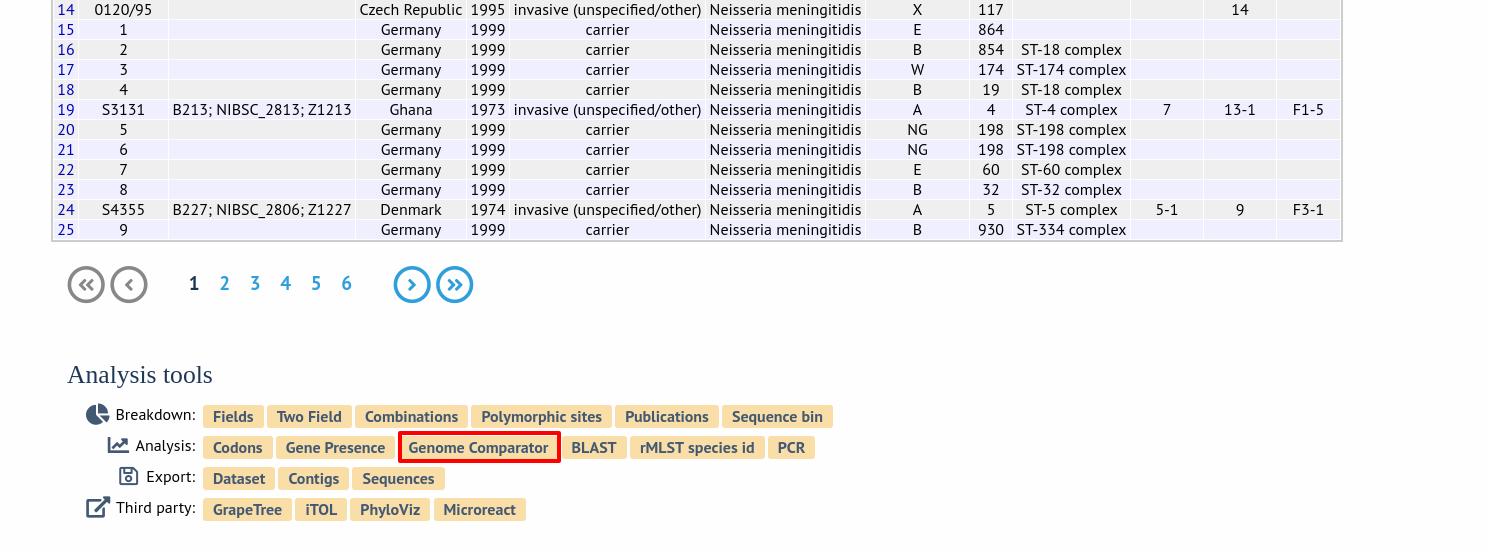
Alternatively, it can be accessed following a query by clicking the ‘Genome Comparator’ button at the bottom of the results table. Isolates with sequence data returned in the query will be automatically selected within the Genome Comparator interface.
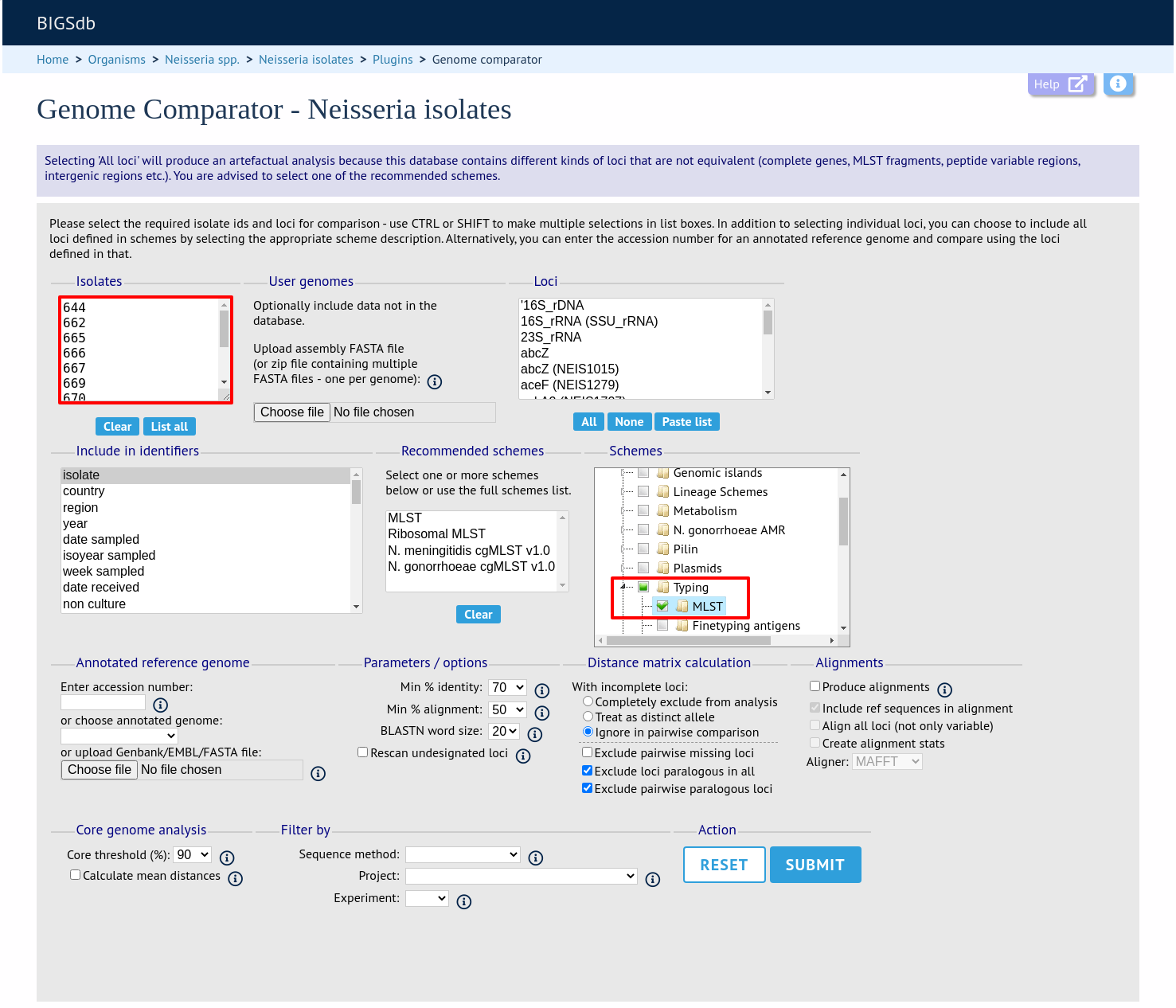
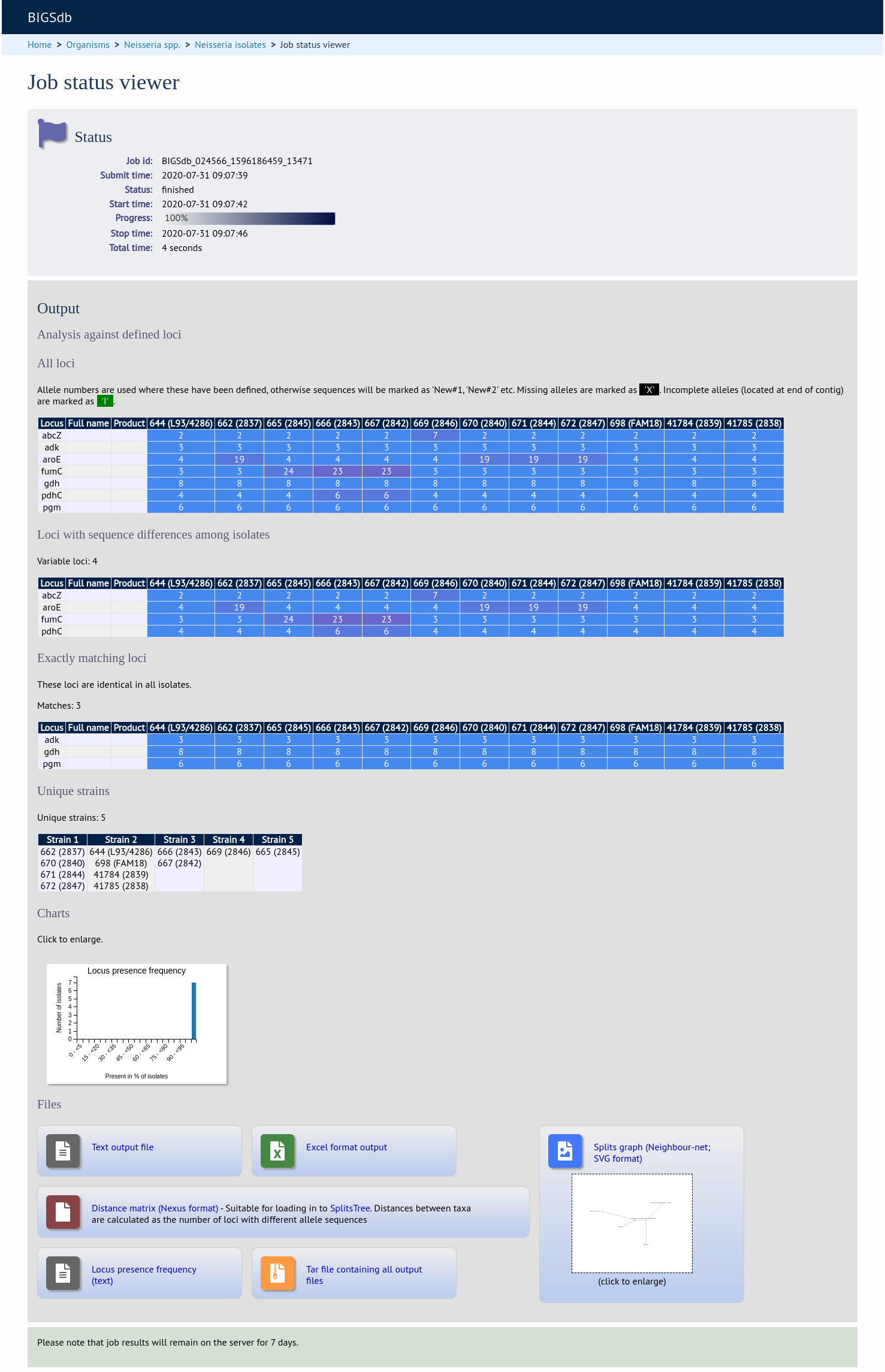
Analysis using defined loci
Select the isolate genomes that you wish to analyse. These will either be in a dropdown list or, if there are too many in the database, a text input where a list can be entered. You can also upload your own genomes for analysis - these should be either a single file in FASTA format (if you have just one genome), or a zip file containing multiple FASTA files. Select either the loci from the list or a set of schemes (either from the schemes box or from a list of recommended schemes if these have been set up). Press submit.
The job will be submitted to the job queue and will start running shortly.
There will be a series of tables displaying variable loci, colour-coded to indicate allelic differences. Finally, there will be links to a distance matrix which can be loaded in to SplitsTree for further analysis and to a NeighborNet chart showing relatedness of isolates. Due to processing constraints on the web server, this NeighborNet is only calculated if 200 or fewer genomes are selected for analysis, but this can be generated in the stand-alone version of SplitsTree using the distance matrix if required.
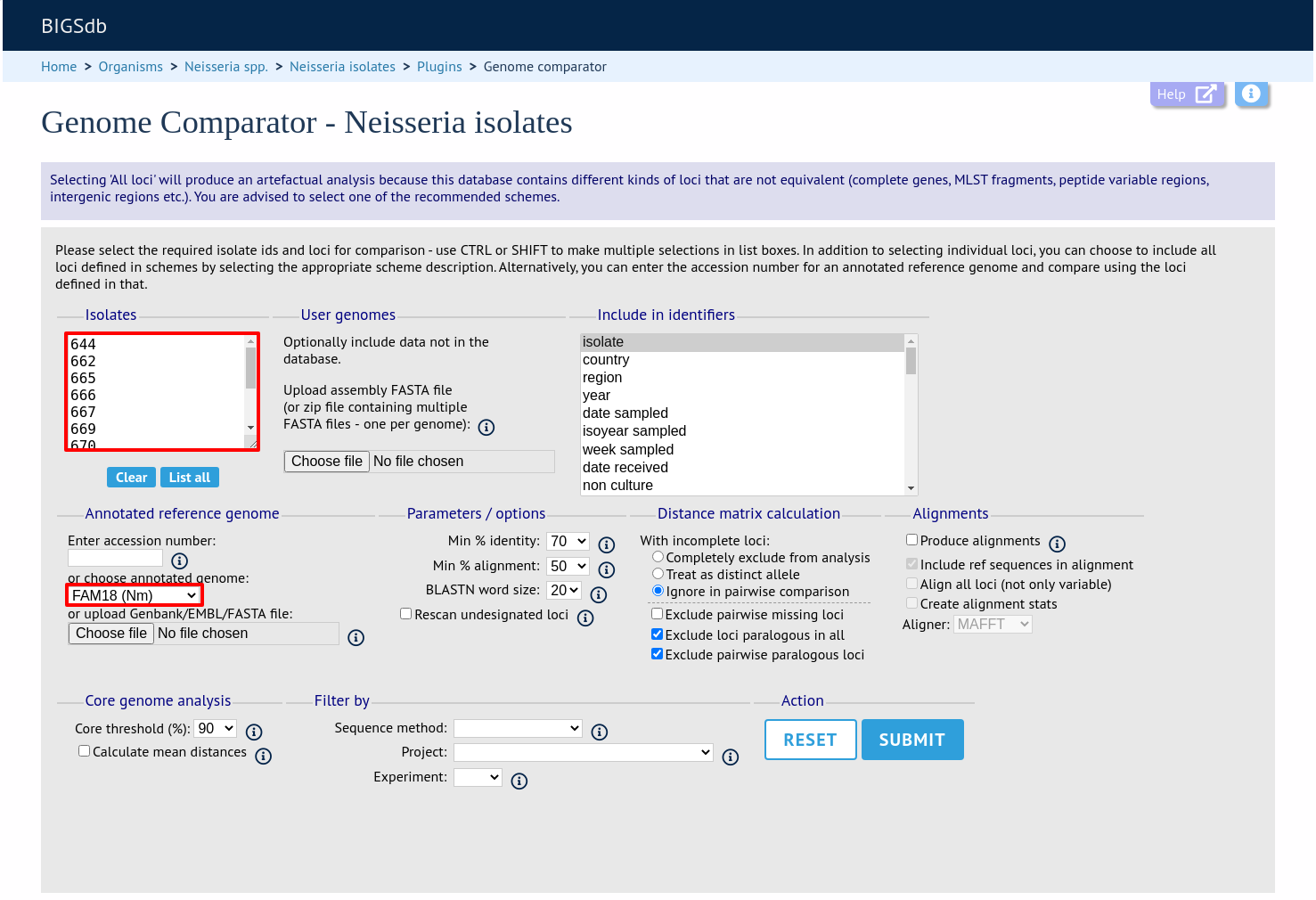
Analysis using annotated reference genome
Select the isolate genomes that you wish to analyse and then either enter a Genbank accession number for the reference genome, or select from the list of reference genomes (this list will only be present if the administrator has set it up). Selecting reference genomes will hide the locus and scheme selection forms.
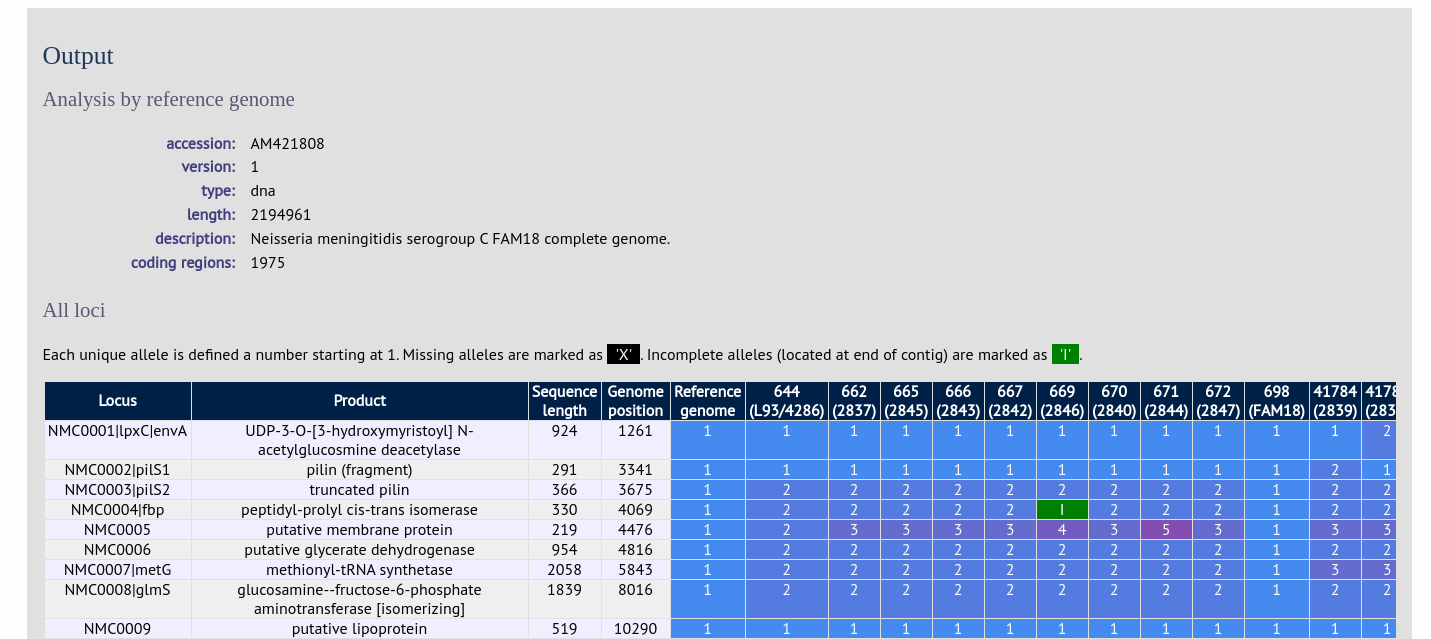
Output is similar to when comparing against defined loci, but this time every coding sequence in the annotated reference will be BLASTed against the selected genomes. Because allele designations are not defined, the allele found in the reference genome is designated allele 1, the next different sequence is allele 2 etc.
Include in identifiers fieldset
This selection box allows you to choose which isolate provenance fields will be included in the results table. This does not affect the output of the alignments as taxa names are limited in length by the alignment programs.
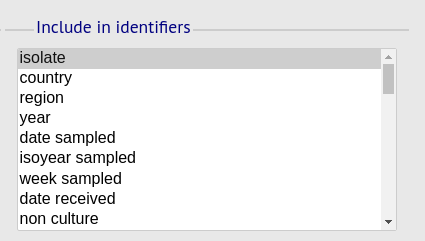
Multiple values can be selected by clicking while holding down Ctrl.
Reference genome fieldset
This section allows you to choose a reference genome to use as the source of comparator sequences.
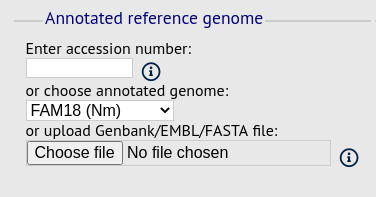
There are three possibilities here:
Enter accession number - Enter a Genbank accession number of an annotated reference and Genome Comparator will automatically retrieve this from Genbank.
Select from list - The administrator may have selected some genomes to offer for comparison. If these are present, simply select from the list.
Upload genome - Click ‘Browse’ and upload your own reference. This can either be in Genbank, EMBL or FASTA format. Ensure that the filename ends in the appropriate file extension (.gb, .embl, .fas) so that it is recognized.
Parameters/options fieldset
This section allows you to modify BLAST parameters. This affects sensitivity and speed.
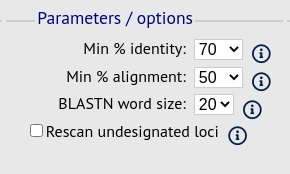
Min % identity - This sets the threshold identity that a matching sequence has to be in order to be considered (default: 70%). Only the best match is used.
Min % alignment - This sets the percentage of the length of reference allele sequence that the alignment has to cover in order to be considered (default: 50%).
BLASTN word size - This is the length of the initial identical match that BLAST requires before extending a match (default: 20). Increasing this value improves speed at the expense of sensitivity. The default value gives good results in most cases. The default setting used to be 15 but the new default of 20 is almost as good (there was 1 difference among 2000 loci in a test run) but the analysis runs twice as fast.
Distance matrix calculation fieldset
This section provides options for the treatment of incomplete and paralogous loci when generating the distance matrix.

For incomplete loci, i.e. those that continue beyond the end of a contig so are incomplete you can:
Completely exclude from analysis - Any locus that is incomplete in at least one isolate will be removed from the analysis completely. Using this option means that if there is one bad genome with a lot of incomplete sequences in your analysis, a large proportion of the loci may not be used to calculate distances.
Treat as a distinct allele - This treats all incomplete sequences as a specific allele ‘I’. This varies from any other allele, but all incomplete sequences will be treated as though they were identical.
Ignore in pairwise comparison (default) - This is probably the best option. In this case, incomplete alleles are only excluded from the analysis when comparing the particular isolate that has it. Other isolates with different alleles will be properly included. The effect of this option will be to shorten the distances of isolates with poorly sequenced genomes with the others.
Paralogous loci, i.e. those with multiple good matches, can be excluded from the analysis (default). This is the safest option since there is no guarantee that differences seen between isolates at paralogous loci are real if the alternative matches are equally good. NB: Loci are also only classed as paralogous when the alternative matches identify different sequences, otherwise multiple contigs of the same sequence region would result in false positives.
Alignments fieldset
This section enables you to choose to produce alignments of the sequences identified.

Available options are:
Produce alignments - Selecting this will produce the alignment files, as well as XMFA and FASTA outputs of aligned sequences. This will result in the analysis taking longer to run.
Include ref sequences in alignment - When doing analysis using an annotated reference, selecting this will include the reference sequence in the alignment files.
Align all loci - By default, only loci that vary among the isolates are aligned. You may however wish to align all if you would like the resultant XMFA and FASTA files to include all coding sequences.
Aligner - There are currently two choices of alignment algorithm (provided they have both been installed)
MAFFT (default) - This is the preferred option as it is significantly quicker than MUSCLE, uses less memory, and produces comparable results.
MUSCLE - This was originally the only choice. It is still included to enable previous analyses to be re-run and compared but it is recommended that MAFFT is used otherwise.
Core genome analysis fieldset
This section enables you to modify the inclusion threshold used to calculate whether or not a locus is part of the core genome (of the dataset).

The default setting of 90% means that a locus is counted as core if it appears within 90% or more of the genomes in the dataset.
There is also an option to calculate the mean distance among sequences of the loci. Selecting this will also select the option to produce alignments.
Filter fieldset
This section allows you to further filter your collection of isolates and the contigs to include.
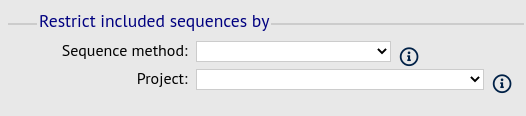
Available options are:
Sequence method - Choose to only analyse contigs that have been generated using a particular method. This depends on the method being set when the contigs were uploaded.
Project - Only include isolates belonging to the chosen project. This enables you to select all isolates and filter to a project.
Understanding the output
Distance matrix
The distance matrix is simply a count of the number of loci that differ between each pair of isolates. It is generated in NEXUS format which can be used as the input file for SplitsTree. This can be used to generate NeighborNet, Split decomposition graphs and trees offline. If 200 isolates or fewer are included in the analysis, a Neighbor network is automatically generated from this distance matrix.
Unique strains
The table of unique strains is a list of isolates that are identical at every locus. Every isolate is likely to be classed as unique if a whole genome analysis is performed, but with a constrained set of loci, such as those for MLST, this will group isolates that are indistinguishable at that level of resolution. nce matrix calculated based on allelic differences and a NeighborNet graph generated from this distance matrix.